 An
Indian Patent titled "A compact drive mechanism of a
reciprocating machine" was granted to IIT Bombay on 5
June
2006. According to the inventor, Prof S L Bapat, Department
of Mechanical Engineering, the objective of the invention is
to
provide a compact and efficient drive mechanism for a reciprocating
machine that is free from side thrust.
The utility of this drive mechanism ranges from reciprocating
compressor and pump (also vacuum pump) to stirling
cycle machines (coolers as well as engines), internal combustion
engines and pulse tube cryocoolers. The drive mechanism
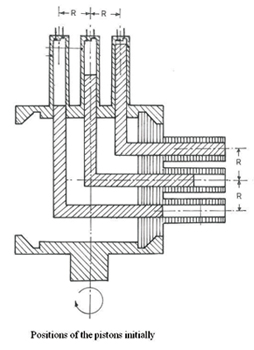
consists of two horizontal circular discs parallel to each
other, both having a coinciding circumferential groove of
same size and shape. One of these discs is stationary while
the
An
Indian Patent titled "A compact drive mechanism of a
reciprocating machine" was granted to IIT Bombay on 5
June
2006. According to the inventor, Prof S L Bapat, Department
of Mechanical Engineering, the objective of the invention is
to
provide a compact and efficient drive mechanism for a reciprocating
machine that is free from side thrust.
The utility of this drive mechanism ranges from reciprocating
compressor and pump (also vacuum pump) to stirling
cycle machines (coolers as well as engines), internal combustion
engines and pulse tube cryocoolers. The drive mechanism
consists of two horizontal circular discs parallel to each
other, both having a coinciding circumferential groove of
same size and shape. One of these discs is stationary while
the
other (driving disc) is rotated using a prime mover. A vertical
(driven) disc with external surface matching the curvature
of
the grooves is placed in between
the two horizontal plates. It
rotates in the grooves about the
central axis of the mechanism
and also about its own horizontal
axis, which ends up in a planetary
motion. This vertical disc
has equally spaced circular
holes, with same pitch circle
diameter through it.
Similarly, the horizontal
stationary disc has same number
of holes to hold tubes acting as
cylinders. Two circular rods are
coupled to each other at right
angle to obtain a L-shaped member.
The horizontal limbs of such
L-shaped members are inserted
through holes in the vertical disc
and the guide sleeve where they
rotate and reciprocate and act as
load bearing limbs. The vertical
limbs act as pistons and reciprocate (and simultaneously
rotate) in the respective cylinders mounted on horizontal stationary
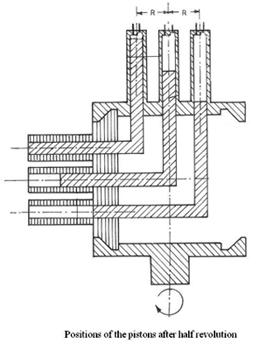
disc. One rotation of the vertical disc is equivalent to
two strokes (one upward and one downward) of each piston.
Thus, the rotary motion is converted to reciprocating one
using this compact drive mechanism. The drive mechanism
enable it to have large stroke to diameter ratio. Moreover,
the
orientation of the drive mechanism has no effect on the performance
of the application for which it is used. The line contact
between the mating members ensures least frictional loss.
The number of piston-cylinder combinations and angular
phase difference between them can be adjusted within the
geometrical constraints.
Contact: slbapat@iitb.ac.in.